

The objective of this study was to determine whether ETCO 2 could be used to distinguish between PSP and SSP. Therefore, we hypothesized that ETCO 2 could be decreased by SP and that such decrease could be large, especially in SSP with lung dysfunction. Pneumothorax is one of the diseases with alveolar hypoventilation from the reduction of vital capacity by air in the pleural space. However, in respiratory dead space and those with a low cardiac output that can present as ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch, Pa-ETCO 2 gradient may be increased due to a reduction of ETCO 2. The gradient between PaCO 2 and ETCO 2 (Pa-ETCO 2 gradient) should be maintained at 2–5 mmHg. ETCO 2 is correlated with partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood (PaCO 2).

Under normal physiologic conditions, the ETCO 2 level is 35–40 mmHg.
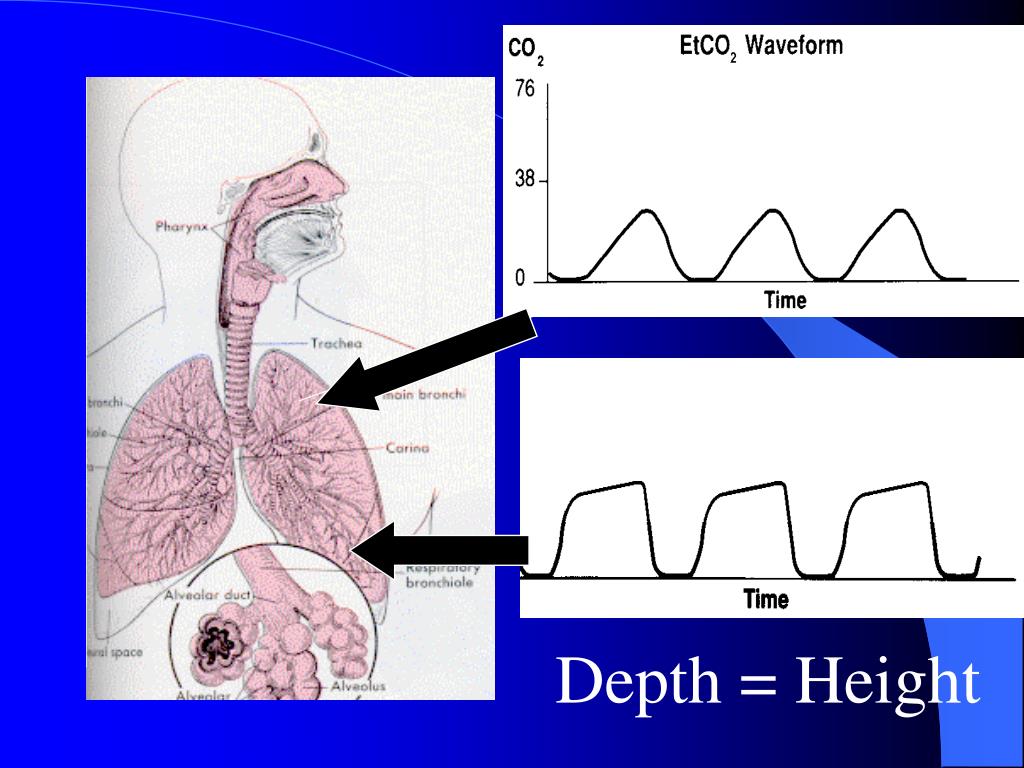
ETCO 2 directly reflects emission of carbon dioxide (CO 2) by ventilation and indirectly reflects the gas exchange capacity of lung and transport of CO 2 via pulmonary circulation. Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO 2) can be measured via capnography. Therefore, it is important to distinguish between PSP and SSP for a timely diagnosis to guide appropriate management. Regarding management strategies, not only characteristics of pneumothorax itself, but also the underlying lung disease associated with SPP should be considered. Thus, SPP needs longer hospitalization period, requires more surgical intervention, and leads to higher mortality. In clinical course of SSP, SSP is usually more unstable than PSP. Spontaneous pneumothorax (SP) without external factor is traditionally classified as primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP) or secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP) based on the absence or presence of associated underlying lung conditions. Initial ETCO 2 lower than 32 mmHg is a predictor of SSP. ETCO 2 monitoring is a reliable noninvasive indicator of differentiating between PSP and SSP. The optimal cutoff for initial ETCO 2 to detection of SSP was 32 mmHg (area under curve, 0.754), with 76.5% sensitivity and 72.7% specificity. Multivariate analysis revealed that respiratory gas associated with SSP was initial ETCO 2 (OR: 0.824 95% CI: 0.697–0.974, ). Initial ETCO 2 was lower in the SSP group than in the PSP group (30 (23–33) vs. There were 33 (66%) patients in the PSP group and 17 (34%) patients in the SSP group. We divided patients into PSP and SSP groups and compared ETCO 2 variables between the two groups. This retrospective observational study included adult patients diagnosed with spontaneous pneumothorax in the emergency room from April 2019 to September 2020. The aim of this study was to investigate the difference in ETCO 2 between PSP and SSP. The pulmonary dysfunction can lead to changes in end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO 2). Spontaneous pneumothorax should be classified as primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP) or secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP) because treatment strategies may differ depending on underlying lung conditions and clinical course.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
